1 React简介
1.1 什么是React

React是一个用于构建用户界面(将数据渲染为HTML视图)的JavaScript库
假如你需要做一个项目,在页面上显示学生的信息,过程大约分为三步
- 发送请求获取数据
- 处理数据(过滤、整理格式等)
- 操作DOM呈现页面
React实际上只关注第三步的内容
1.2 原生JavaScript的缺点
- 原生JavaScript操作DOM繁琐。效率低(DOM-API操作UI)
document.getElementById('app')
document.querySelector('#app')
document.getElementsByTagName('span')
- 使用JavaScript直接操作DOM,浏览器会进行大量的编译重排
- 原生JavaScript没有组件化编码方案,代码复用率低
1.3 React优势
- 采用组件化模式、声明式编码,提高开发效率及组件复用率
- React Native中可以使用React语法进行移动端开发
- 使用虚拟DOM + 优秀的Diffing算法,尽量减少与真实的DOM交互
2 React入门
2.1 React的基本使用
2.1.1 相关js库
- react.js:React核心库。
- react-dom.js:提供操作DOM的react扩展库。
- babel.min.js:解析JSX语法代码转为JS代码的库。
2.1.2 快速入门
创建一个Html,具体内容见注释
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=
, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Hello React</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备容器 -->
<div id="test">
</div>
<!-- 注意, react.development.js一定要在react-dom.development.js之前引入 -->
<!-- 引入React核心库 -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<!-- 引入React-DOM,用于支持React操作DOM -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<!-- 引入label,用于将jsx转为js -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<!-- 此处一定要写babel -->
<script type="text/babel">
// 1.创建虚拟DOM
// 此处一定不要写引号, 因为不是字符串
let VDOM = <h1>Hello, React</h1>
// 2.渲染虚拟DOM到页面
// ReactDOM.render(虚拟Dom, 容器)
ReactDOM.render(VDOM, document.getElementById('test'))
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.1.3 虚拟DOM的两种创建方式
2.1.3.1 使用JSX创建虚拟DOM
与上文代码一样
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=
, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>使用JSX创建虚拟DOM</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备容器 -->
<div id="test">
</div>
<!-- 注意, react.development.js一定要在react-dom.development.js之前引入 -->
<!-- 引入React核心库 -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<!-- 引入React-DOM,用于支持React操作DOM -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<!-- 引入label,用于将jsx转为js -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<!-- 此处一定要写babel -->
<script type="text/babel">
// 1.创建虚拟DOM
let VDOM = ( // 此处一定不要写引号, 因为不是字符串
<h1 title="id">
<span>Hello, React</span>
</h1>
)
// 2.渲染虚拟DOM到页面
// ReactDOM.render(虚拟Dom, 容器)
ReactDOM.render(VDOM, document.getElementById('test'))
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.1.3.2 使用JS创建虚拟DOM
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=
, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>使用JS创建虚拟DOM</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备容器 -->
<div id="test">
</div>
<!-- 注意, react.development.js一定要在react-dom.development.js之前引入 -->
<!-- 引入React核心库 -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<!-- 引入React-DOM,用于支持React操作DOM -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<!-- 此处一定要写babel -->
<script type="text/javascript">
// 1.创建虚拟DOM
// React.createElement(标签名, 标签属性, 标签内容)
let VDOM = React.createElement('h1', {id: 'title'}, React.createElement('span', {}, "Hello, React"))
// 2.渲染虚拟DOM到页面
// ReactDOM.render(虚拟Dom, 容器)
ReactDOM.render(VDOM, document.getElementById('test'))
</script>
</body>
</html>
可以发现,当嵌套多层的时候,该语法会变得非常繁琐,因此在实际开发过程中,我们还是采用JSX的写法即可
2.1.4 虚拟DOM与真实DOM
打印一下虚拟DOM
console.log("虚拟DOM: ", VDOM)
let TDOM = document.getElementById('test');
console.log("真实DOM: ", TDOM);
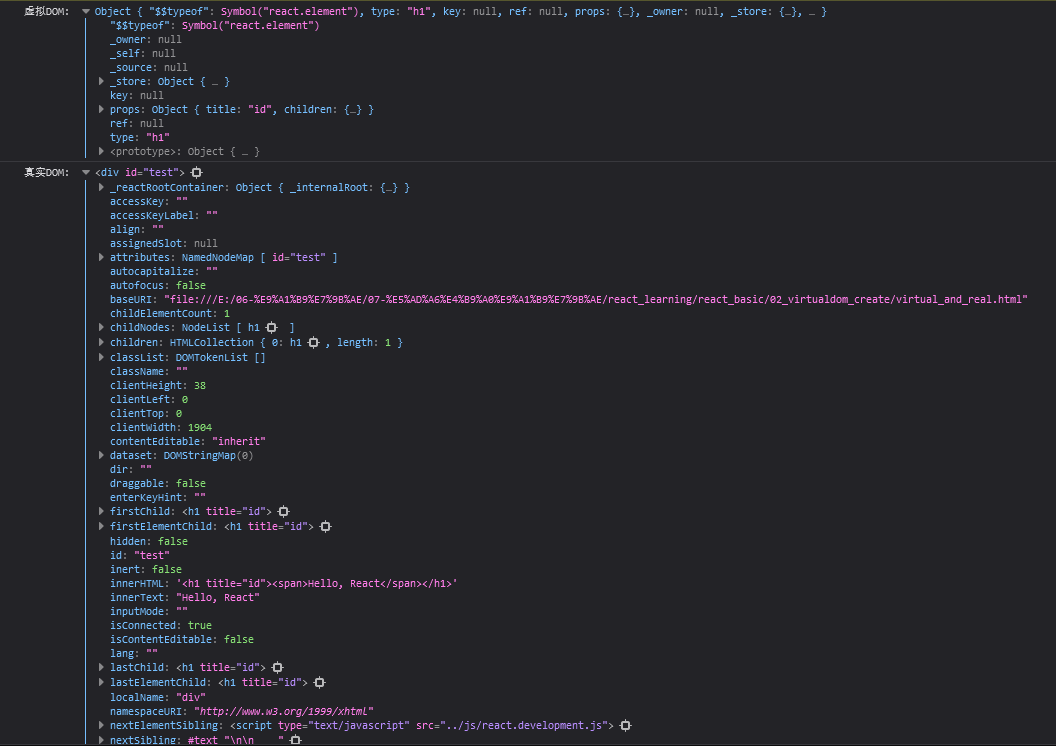
可以发现
- 虚拟DOM本质是Object类型的对象
- 虚拟DOM比真实DOM轻,因为虚拟DOM是React内部在用,无需真实DOM上那么多属性
- 虚拟DOM最终会被React转换为真实DOM,呈现在页面上
2.2 React JSX
JSX,全称JavaScript XML,是react定义的一种类似于XML的JS扩展语法:
JS + XML本质是React.createElement(component, props, ...children)方法的语法糖
JSX语法规则:
- 定义虚拟DOM时,不要写引号
- 标签中混入JS表达式时,使用
{}
let myId = 'id'
let myData = 'Hello, React'
let VDOM = (
<h2 id={myId.toLowerCase()}>
<span>{myData.toLocaleLowerCase()}</span>
</h2>
)
- 样式的类名指定使用
className
let VDOM = (
<h2 className="title" id={myId.toLowerCase()}>
<span>{myData.toLocaleLowerCase()}</span>
</h2>
)
- 内联样式需要使用
style={{key:value}}的形式
let VDOM = (
<h2 className="title" id={myId.toLowerCase()}>
<span style={{color: 'white'}}>{myData.toLocaleLowerCase()}</span>
</h2>
)
- JSX不允许出现多个根标签,当出现多个标签时,可以使用一个
div包裹起来
let VDOM = (
<div>
<h2 className="title" id={myId.toLowerCase()}>
<span style={{color: 'white'}}>{myData.toLocaleLowerCase()}</span>
</h2>
<input type="text"/>
</div>
)
- 标签必须闭合
- 标签首字母若为小写字母开头,则将该标签转为html中同名元素,若无该标签对应的同名元素则报错
- 标签首字母若为大写字母开头,React就去渲染对应的组件,若组件没有定义则保存
2.3 模块与组件、模块化与组件化
2.3.1 模块
模块就是向外提供特定功能的js程序, 一般就是一个js文件
随着业务逻辑增加,代码越来越多且复杂,使用模块可以复用js, 简化js的编写, 提高js运行效率
2.3.2 组件
组件是用来实现局部功能效果的代码和资源的集合(html/css/js/image等等)
例如下面一个页面
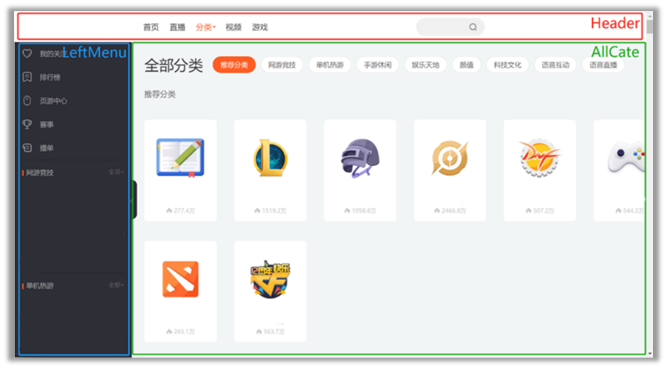
在原先写在同一个html里面,用不同的div分割,现在可以使用组件,拆分成不同的组件,可以达到复用编码, 简化项目编码, 提高运行效率的效果
3 React面向组件编程
3.1 安装开发者调试工具
以Firefox为例

3.2 组件的基本使用
3.2.1 函数式组件
// 1.创建函数式组件
function Demo() {
return <h2>我是用函数定义的组件, 适用于简单组件的定义</h2>
}
// 2.渲染组件到页面
ReactDOM.render(<Demo/>, document.getElementById('test'))
执行ReactDOM.render后,React的工作:
- React解析组件标签,找到了
Demo组件 - 发现组件是用函数定义的,随后调用该函数,将返回的虚拟DOM转为真实DOM,随后呈现在页面中
3.2.2 类式组件
// 1.创建类式组件, 需要继承React.Component
class Demo extends React.Component {
render() {
return <h2>我是用类定义的组件, 适用于复杂组件的定义</h2>
}
}
// 2.渲染组件到页面
ReactDOM.render(<Demo/>, document.getElementById('test'))
执行ReactDOM.render后,React的工作:
- React解析组件标签,找到了
Demo组件 - 发现组件是用类定义的,随后new出该类的实例,并通过该实例调用到原型上的render方法
- 将render返回的虚拟DOM转为真实DOM,随后呈现在页面中
3.3 组件实例三大核心属性
之前的类式组件中,打印一下this
class Demo extends React.Component {
render() {
console.log(this)
return <h2>我是用类定义的组件, 适用于复杂组件的定义</h2>
}
}
输出如下:
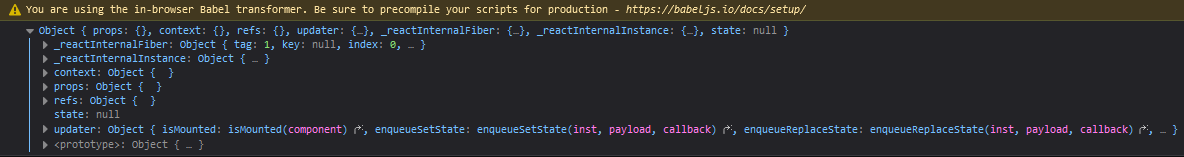
其中props、refs、state就是组件实例的三大核心属性
3.3.1 State
state是组件对象最重要的属性, 值是对象(可以包含多个key-value的组合)
组件被称为"状态机", 通过更新组件的state来更新对应的页面显示(重新渲染组件)
下面一个案例,点击更换天气
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=
, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>State</title>
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="../images/favicon.ico" type="image/x-icon">
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备容器 -->
<div id="test">
</div>
<!-- 注意, react.development.js一定要在react-dom.development.js之前引入 -->
<!-- 引入React核心库 -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<!-- 引入React-DOM,用于支持React操作DOM -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<!-- 引入label,用于将jsx转为js -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<!-- 此处一定要写babel -->
<script type="text/babel">
// 1.创建类式组件, 需要继承React.Component
class Weather extends React.Component {
// 自定义构造器
constructor(props) {
super(props)
// 更新组件状态
this.state = {isHot: false}
this.changeWeather = this.changeWeather.bind(this)
}
render() {
let msg = this.state.isHot? "炎热": "凉爽"
return <h1 onClick={this.changeWeather}>今天天气很{msg}</h1>
}
changeWeather() {
// 只有通过Weather实例调用changeWeather方法,changeWeather的方法才是Weather实例
// 由于changeWeather是作为onClick的回调,所以不是通过实例调用的,是直接调用
// 类中的方法默认开启了局部的严格模式,所以changeWeather中的this为undefined
console.log(this)
// 状态不可直接更改,需要使用setState
this.setState({isHot: !this.state.isHot })
}
}
// 2.渲染组件到页面
ReactDOM.render(<Weather/>, document.getElementById('test'))
</script>
</body>
</html>
注意:
-
组件中render方法中的this为组件实例对象
-
组件自定义的方法中this为undefined,如何解决?
-
强制绑定this: 通过函数对象的bind()
-
箭头函数
-
-
状态数据,不能直接修改或更新,需要使用setState
-
setState为合并的动作而非替换
-
构造器调用一次,render调用1+n次,1是初始化,n是状态更新的次数
上面写法可以简化,简化后写法:
<script type="text/babel">
class Weather extends React.Component {
state = {isHot: false}
changeWeather = () => {
this.setState({isHot: !this.state.isHot })
}
render() {
let msg = this.state.isHot? "炎热": "凉爽"
return <h1 onClick={this.changeWeather}>今天天气很{msg}</h1>
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Weather/>, document.getElementById('test'))
</script>
3.3.2 Props
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=
, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Props</title>
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="../images/favicon.ico" type="image/x-icon">
</head>
<body>
<div id="test">
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react.development.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/babel.min.js"></script>
<!-- 引入prop-types, 用于对组件标签进行限制 -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/prop-types.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
class Person extends React.Component {
// 限制组件
static propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
sex: PropTypes.string,
age: PropTypes.number,
speak: PropTypes.func
}
// 默认值
static defaultProps = {
sex: '不男不女'
}
state = {
}
render() {
console.log(this)
let {name, age, sex} = this.props
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名: {name}</li>
<li>性别: {sex}</li>
<li>年龄: {age + 1}</li>
</ul>
)
}
}
let p = {name: '老刘', age: 18, sex: '男'}
ReactDOM.render(<Person {...p}/>, document.getElementById('test'))
</script>
</body>
</html>
这里可以使用{...p}传递props
注意
{...p}并非是展开运算符的复制对象,而是react自带的语法,可以遍历属性,但这种方式只能在props里使用,其他地方无法使用该语法遍历对象属性- props为只读的
可以发现,类式组件(拥有实例)拥有props,那函数式组件是否可以拥有props呢?答案是可以的
函数式组件在三大组件中仅能使用props
function Person (props) {
console.log(props)
let {name, age, sex} = props
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名: {name}</li>
<li>性别: {sex}</li>
<li>年龄: {age + 1}</li>
</ul>
)
}
let p = {name: '老刘', age: 18, sex: '男'}
ReactDOM.render(<Person {...p}/>, document.getElementById('test'))
3.3.3 Refs
组件内的标签可以定义ref属性来标识自己
3.3.3.1 字符串类型Refs
这种方式官方已经不推荐使用
<script type="text/babel">
class Demo extends React.Component {
showData1 = () => {
let {input1} = this.refs
alert(input1.value)
}
showData2 = () => {
let {input2} = this.refs
alert(input2.value)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<input ref="input1" type="text" placeholder="点击按钮提示数据"/>
<button onClick={this.showData1} >点我提示左侧数据</button>
<input ref="input2" type="text" onBlur={this.showData2} placeholder="失去焦点提示数据"/>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Demo/>, document.getElementById("test"))
</script>
3.3.3.2 回调函数形式Refs
<script type="text/babel">
class Demo extends React.Component {
showData1 = () => {
alert(this.input1.value)
}
showData2 = () => {
alert(this.input2.value)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<input ref={(curNode) => {this.input1 = curNode}} type="text" placeholder="点击按钮提示数据"/>
<button onClick={this.showData1} >点我提示左侧数据</button>
<input ref={(curNode) => {this.input2 = curNode}} type="text" onBlur={this.showData2} placeholder="失去焦点提示数据"/>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Demo/>, document.getElementById("test"))
</script>
注意:如下代码
<script type="text/babel">
class Demo extends React.Component {
state = {
isHot: false
}
showData1 = () => {
alert(this.input1.value)
}
changeWeather = () => {
let {isHot} = this.state
this.setState({isHot: !isHot})
}
render() {
let {isHot} = this.state
return (
<div>
<h2>今天天气很{isHot ? '炎热': '凉爽'}</h2>
<input ref={(curNode) => {this.input1 = curNode; console.log(curNode)}} type="text" placeholder="点击按钮提示数据"/>
<button onClick={this.showData1} >点我提示左侧数据</button>
<button onClick={this.changeWeather} >点我切换天气</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Demo/>, document.getElementById("test"))
</script>
如果回调Ref函数是以内联函数 的方式定义的,在更新过程中它会被执行两次,第一次传入参数null,第二次传入参数DOM元素。这是因为每次渲染时会创建一个新的函数实例,所以react会清空旧的并设置新的。
3.3.3.3 createRef
可以使用React.createRef(),调用后可以返回一个容器,该容器可以存储被Ref标识的结点,该容器是专人专用
<script type="text/babel">
class Demo extends React.Component {
myRef = React.createRef()
showData1 = () => {
alert(this.myRef.current.value)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<input ref={this.myRef} type="text" placeholder="点击按钮提示数据"/>
<button onClick={this.showData1} >点我提示左侧数据</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Demo/>, document.getElementById("test"))
</script>
3.3.3.4 事件处理
- 通过onXxx属性指定事件处理函数(注意大小写)
- React使用的是自定义(合成)事件, 而不是使用的原生DOM事件
- React中的事件是通过事件委托方式处理的(委托给组件最外层的元素)
- 通过event.target得到发生事件的DOM元素对象
<script type="text/babel">
class Demo extends React.Component {
myRef = React.createRef()
showData1 = () => {
alert(this.myRef.current.value)
}
showData2 = (event) => {
alert(event.target.value)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<input ref={this.myRef} type="text" placeholder="点击按钮提示数据"/>
<button onClick={this.showData1} >点我提示左侧数据</button>
<input onBlur={this.showData2} type="text" placeholder="失去焦点提示数据"/>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Demo/>, document.getElementById("test"))
</script>
3.4 收集表单数据
3.4.1 非受控组件
即用即取
<script type="text/babel">
class Login extends React.Component {
handleSubmit = (event) => {
event.preventDefault()
const {username , password} = this
alert(`你输入的用户名是: ${username.value}, 密码是:${password.value}`)
}
render() {
return (
<form action="" onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
用户名: <input ref={c => this.username = c} type="text" name="username"/>
密码: <input ref={c => this.password = c} type="password" password="password"/>
<button>登录</button>
</form>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Login/>, document.getElementById("test"))
</script>
3.4.2 受控组件
随着输入修改状态,叫非受控组件
<script type="text/babel">
class Login extends React.Component {
state = {
username: '',
password: ''
}
handleSubmit = (event) => {
event.preventDefault()
const {username , password} = this.state
alert(`你输入的用户名是: ${username}, 密码是:${password}`)
}
saveUsername = (event) => {
this.setState({username: event.target.value})
}
savePassword = (event) => {
this.setState({username: event.target.value})
}
render() {
return (
<form action="" onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
用户名: <input onChange={this.saveUsername} type="text" name="username"/>
密码: <input onChange={this.savePassword} type="password" password="password"/>
<button>登录</button>
</form>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Login/>, document.getElementById("test"))
</script>
3.5 高阶函数和函数的柯里化
高阶函数:如果一个函数符合下面两个规范中的任何一个,那该函数就是高阶函数
- 若A函数,接收的参数是一个函数,那么A就可以称为高阶函数
- 若A函数,调用的返回值依然是一个函数,那么A就可以称为高阶函数
函数的柯里化:通过函数调用继续返回函数的形式,实现多次接收参数最后统一处理的函数编码形式
如下面例子:saveFormData就是一个高阶函数
<script type="text/babel">
class Login extends React.Component {
state = {
username: '',
password: ''
}
handleSubmit = (event) => {
event.preventDefault()
const {username , password} = this.state
alert(`你输入的用户名是: ${username}, 密码是:${password}`)
}
saveFormData = (dataType) => {
console.log(dataType)
return (event) => {
this.setState({[dataType]: event.target.value})
console.log(event.target.value)
}
}
render() {
return (
<form action="" onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
用户名: <input onChange={this.saveFormData('username')} type="text" name="username"/>
密码: <input onChange={this.saveFormData('password')} type="password" password="password"/>
<button>登录</button>
</form>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Login/>, document.getElementById("test"))
</script>
另外一种写法:
saveFormData = (dataType, event) => {
this.setState({[dataType]: event.target.value})
}
render() {
return (
<form action="" onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
用户名: <input onChange={(event) => {this.saveFormData('username', event)}} type="text" name="username"/>
密码: <input onChange={(event) => {this.saveFormData('password', event)}} type="password" password="password"/>
<button>登录</button>
</form>
)
}
3.6 React的生命周期
3.6.1 Demo例子
先看一个示例,该示例让指定的文本做显示 / 隐藏的渐变动画,点击“不活了”按钮从界面中卸载组件
<script type="text/babel">
class Life extends React.Component {
death = () => {
// 取消挂载
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById('test'))
}
state = {
opacity: 1
}
// 组件挂载页面之后调用
componentDidMount() {
this.timmer = setInterval(() => {
this.setState({opacity: this.state.opacity - 0.1})
if (this.state.opacity < 0) this.setState({opacity: 1})
}, 200);
}
// 组件卸载之前
componentWillUnmount() {
clearInterval(this.timmer)
}
// 初始化渲染、状态更新之后调用
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2 style={{opacity: this.state.opacity}}>React学不会怎么办?</h2>
<button onClick={this.death}>不活了</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Life/>, document.getElementById("test"))
</script>
3.6.2 生命周期(16.8)
- 组件从创建到死亡它会经历一些特定的阶段。
- React组件中包含一系列勾子函数(生命周期回调函数), 会在特定的时刻调用。
- 我们在定义组件时,会在特定的生命周期回调函数中,做特定的工作。
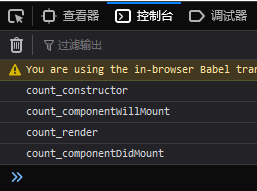
<script type="text/babel">
class Count extends React.Component {
// 构造器
constructor(props) {
console.log('count_constructor')
super(props)
}
state = {
count: 0
}
// 组件将要挂载
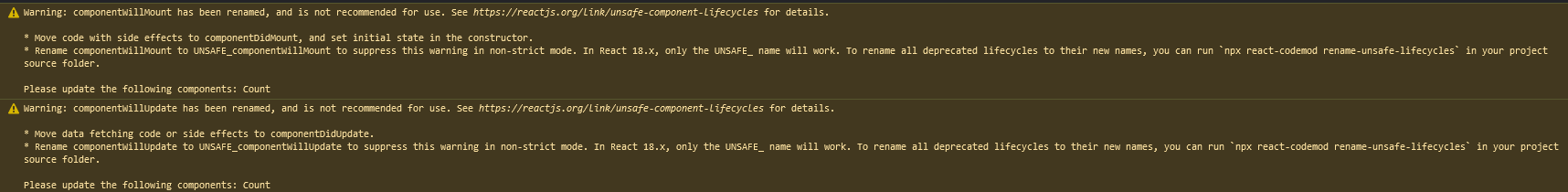
componentWillMount() {
console.log('count_componentWillMount')
}
// 组件挂载页面之后调用
componentDidMount() {
console.log('count_componentDidMount')
}
// 组件卸载之前
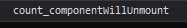
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('count_componentWillUnmount')
}
// 渲染
render() {
console.log('count_render')
return (
<div>
<h2>当前求和为{this.state.count}</h2>
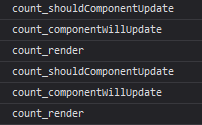
<button onClick={() => {this.setState({count: this.state.count + 1})}}>点我+1</button>
<button onClick={() => {ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById('test'))}}>不活了</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Count/>, document.getElementById('test'))
</script>
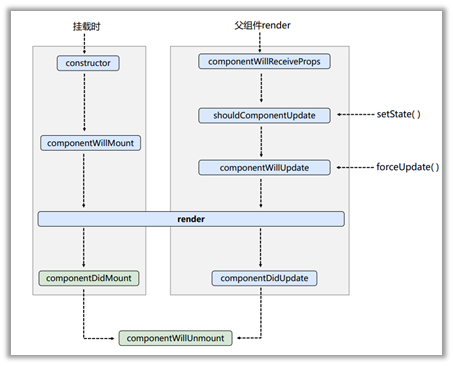
组件初始化:由ReactDOM.render()触发,初次渲染
组件更新:由组件内部this.setSate()或父组件重新render触发
卸载组件: 由ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode()触发
3.6.3 生命周期(17.0)
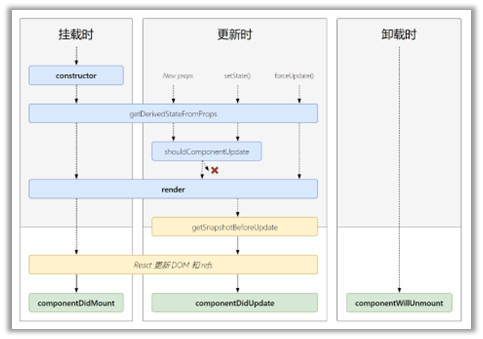
当组件实例被创建并插入 DOM 中时,其生命周期调用顺序如下:
- constructor()
- getDerivedStateFromProps()
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state):getDerivedStateFromProps 会在调用 render 方法之前调用,并且在初始挂载及后续更新时都会被调用。它应返回一个对象来更新 state,如果返回 null 则不更新任何内容。
- render()
- componentDidMount()
当组件的 props 或 state 发生变化时会触发更新。组件更新的生命周期调用顺序如下:
- static getDerivedStateFromProps()
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state):getDerivedStateFromProps 会在调用 render 方法之前调用,并且在初始挂载及后续更新时都会被调用。它应返回一个对象来更新 state,如果返回 null 则不更新任何内容。
-
shouldComponentUpdate()
-
render()
-
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState):getSnapshotBeforeUpdate() 在最近一次渲染输出(提交到 DOM 节点)之前调用。它使得组件能在发生更改之前从 DOM 中捕获一些信息(例如,滚动位置)。此生命周期方法的任何返回值将作为参数传递给 componentDidUpdate()。
<script type="text/babel">
class NewsList extends React.Component{
state = {newsArr: []}
componentDidMount(){
setInterval(() => {
let {newsArr} = this.state
let news = '新闻' + (newsArr.length + 1)
this.setState({newsArr: [news, ...newsArr]})
}, 1000)
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate() {
return this.refs.list.scrollHeight
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProp, preState, height) {
this.refs.list.scrollTop += this.refs.list.scrollHeight - height
}
render() {
return (
<div className="list" ref="list">
{
this.state.newsArr.map((n, index) => {
return <div className="news" key={index}>{n}</div>
})
}
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<NewsList/>, document.getElementById("app"))
</script>
- componentDidUpdate()
当组件从 DOM 中移除时会调用如下方法:
- componentWillUnmount()
3.7 diffing算法
diffing算法是用于两个虚拟dom的比较,最小单位是标签
react/vue中的key有什么作用?
状态中的数据发生变化时,react会根据【新数据】生成【新的虚拟DOM】,随后React进行【新虚拟DOM】与【旧虚拟DOM】的diff比较,比较规则如下:
- 旧虚拟DOM中找到了与新虚拟DOM相同的key:
> - 若虚拟DOM中内容没变, 直接使用之前的真实DOM
- 若虚拟DOM中内容变了, 则生成新的真实DOM,随后替换掉页面中之前的真实DOM
- 旧虚拟DOM中未找到与新虚拟DOM相同的key:根据数据创建新的真实DOM,随后渲染到到页面
用index作为key可能会引发的问题:
- 若对数据进行:逆序添加、逆序删除等破坏顺序操作:会产生没有必要的真实DOM更新
- 如果结构中还包含输入类的DOM:会产生错误DOM更新
4 React应用
4.1 使用create-react-app创建react应用
4.1.1 React脚手架
react提供了一个用于创建react项目的脚手架库: create-react-app, 项目的整体技术架构为: react + webpack + es6 + eslint
使用脚手架开发的项目的特点: 模块化, 组件化, 工程化
4.1.2 创建项目并启动
全局安装:
npm i -g create-react-app
切换到想创项目的目录,使用命令:
create-react-app hello-react
进入项目文件夹,启动项目:
npm start
4.1.3 React脚手架目录结构
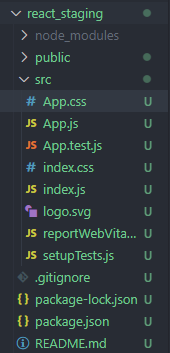
public:静态资源文件夹
- favicon.icon:网站页签图标
- index.html:主页面
- logo192.png:logo图
- logo512.png:logo图
- manifest.json:应用加壳的配置文件
- robots.txt:--- 爬虫协议文件
src :源码文件夹
- App.css:App组件的样式
- App.js:App组件
- App.test.js:用于给App做测试
- index.css : 样式
- **index.js :**入口文件
- logo.svg :logo图
- reportWebVitals.js:页面性能分析文件(需要web-vitals库的支持)
- setupTests.js:组件单元测试的文件(需要jest-dom库的支持
4.1.4 编写代码
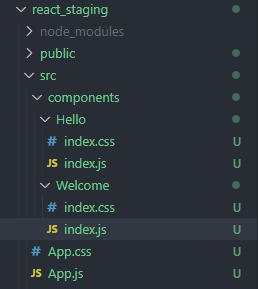
App.js
import './App.css';
import Hello from './components/Hello'
import React, {Component} from 'react'
import Welcome from './components/Welcome';
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<Hello/>
<Welcome/>
</div>
)
}
}
Hello.js
import React, {Component} from 'react'
import './index.css'
export default class Hello extends Component {
render() {
return (
<h2 className="title">
Hello, React!
</h2>
)
}
}
Welcome.js
import React, {Component} from 'react'
import './index.css'
export default class Welcome extends Component {
render() {
return (
<h2 className="title2">
Welcome!
</h2>
)
}
}
4.1.5 样式的模块化
在Hello.js中,我们的className为title,而在Welcome.js中,我们的className为title2,这样组件的样式不会重叠,但如果两个组件的className都为title,那么后引入的模块的样式会覆盖之前的样式.
我们可以采用如下的方式避免这个问题:
import React, {Component} from 'react'
import hello from './index.module.css'
export default class Hello extends Component {
render() {
return (
<h2 className={hello.title}>
Hello, React!
</h2>
)
}
}
4.2 父子组件传值
父:
addTodo = (data) => {
console.log("App", data)
}
render() {
let {todos} = this.state
return (
<div className="todo-container">
<div className="todo-wrap">
<Header a={this.addTodo}/>
<List todos={todos}/>
<Footer/>
</div>
</div>
)
}
子:
export default class Header extends Component {
handleKeyUp = (event) => {
let {keyCode, target} = event
if (keyCode !== 13) return
console.log(target.value)
this.props.a(target.value)
}
render() {
return (
<div className="todo-header">
<input onKeyUp={this.handleKeyUp} type="text" placeholder="请输入你的任务名称,按回车键确认" />
</div>
)
}
}
5 React ajax
5.1 介绍
- React本身只关注于界面, 并不包含发送ajax请求的代码
- 前端应用需要通过ajax请求与后台进行交互(json数据)
- react应用中需要集成第三方ajax库(或自己封装)
常用的ajax请求库
- jQuery: 比较重, 如果需要另外引入不建议使用
- axios: 轻量级, 建议使用
- 封装XmlHttpRequest对象的ajax
- promise风格
- 可以用在浏览器端和node服务器端
5.2 使用axios
安装axios
yarn add axios
使用
import './App.css';
import axios from 'axios'
import React, { Component } from 'react'
export default class App extends Component {
getStudentData = () => {
axios.get("http://localhost:5000/students").then(
response => {console.log('Success', response.data)},
error => {console.log('Error', error)}
)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.getStudentData}>点我获取学生数据</button>
</div>
)
}
}
测试
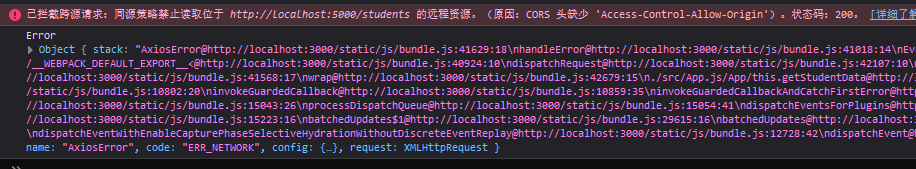
显示跨域,怎么解决这个问题呢?配置代理
跨域实际上请求是可以发的,只是数据回不来而已
5.3 React脚手架配置代理
5.3.1 修改package.json
"proxy": "http://localhost:5000"
注意,这种方法在react 18之后并不适用,工作台一般会运行不了 报这个错误
yarn run v1.22.19
$ react-scripts start
Invalid options object. Dev Server has been initialized using an options object that does not match the API schema.
- options.allowedHosts[0] should be a non-empty string.
error Command failed with exit code 1.
info Visit https://yarnpkg.com/en/docs/cli/run for documentation about this command.
5.3.2 编辑setupProxy.js
const { createProxyMiddleware } = require('http-proxy-middleware')
module.exports = function (app) {
app.use(
createProxyMiddleware('/api1', {
target: 'http://localhost:5000',
changeOrigin: true,
pathRewrite: { '^/api1': '' }
}),
createProxyMiddleware('/api2', {
target: 'http://localhost:5001',
changeOrigin: true,
pathRewrite: { '^/api2': '' }
})
)
}
5.4 消息订阅-发布机制
下载:
npm install pubsub-js --save
使用:
消息发布:
PubSub.publish('update_data', {isLoading: false, users: response.data.items})
消息订阅:
componentDidMount() {
this.token = PubSub.subscribe('update_data', (_, stateObj) => {
console.log("receive data: ", stateObj)
this.setState(stateObj)
})
}
componentWillUnmount() {
PubSub.unsubscribe(this.token)
}
6 React路由
6.1 基础概念
6.1.1 SPA
- 单页Web应用(single page web application,SPA)。
- 整个应用只有一个完整的页面。
- 点击页面中的链接不会刷新页面,只会做页面的局部更新。
- 数据都需要通过ajax请求获取, 并在前端异步展现。
6.1.2 路由
什么是路由?
- 一个路由就是一个映射关系(key:value)
- key为路径, value可能是function或component
路由分类
- 后端路由:
理解: value是function, 用来处理客户端提交的请求。
注册路由: router.get(path, function(req, res))
工作过程:当node接收到一个请求时, 根据请求路径找到匹配的路由, 调用路由中的函数来处理请求, 返回响应数据
- 前端路由:
浏览器端路由,value是component,用于展示页面内容。
注册路由: <Route path="/test" component={Test}>
工作过程:当浏览器的path变为/test时, 当前路由组件就会变为Test组件
6.2 react-router-dom
react-router-dom是react的一个插件库,专门用来实现一个SPA应用。基于react的项目基本都会用到此库。
安装
yarn add react-router-dom
引入
import { Link, BrowserRouter, Route } from 'react-router-dom'
使用
<div>
<BrowserRouter>
<div className="row">
<div className="col-xs-offset-2 col-xs-8">
<div className="page-header"><h2>React Router Demo</h2></div>
</div>
</div>
<div className="row">
<div className="col-xs-2 col-xs-offset-2">
<div className="list-group">
{/* <a className="list-group-item" href="./about.html">About</a>
<a className="list-group-item active" href="./home.html">Home</a> */}
<Link className="list-group-item" to="/about">About</Link>
<Link className="list-group-item" to="/home">Home</Link>
</div>
</div>
<div className="col-xs-6">
<div className="panel">
<div className="panel-body">
<Route path="/about" component={About} />
<Route path="/home" component={Home} />
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</BrowserRouter>
</div>
6.2.1 Route
Route组件:可以指定路径和组件,在路径不同时展示组件使用,在Route外侧需要有Router包裹,可选用的Router有
HashRouterBrowserRouter
6.2.2 Link
Link组件:React中靠路由链接实现切换组件,Link可以切换当前的路径,在Link外侧也需要有Router包裹
实际上最后渲染的Html为
<a className="list-group-item active" href="/about" aria-current="page">About</a>
6.2.3 NavLink
NavLink组件:为Link组件的升级版,可以为选中的Link添加指定的样式,方式为
<NavLink activeClass="active" className="list-group-item" to="/about">About</NavLink>
若不指定activeClass,则默认为active
6.2.4 Switch
Switch组件:当我们使用Route组件时,包含相同的path,会依次匹配,展示所有相同path的组件,我们可以使用Switch组件,指定当匹配到第一个组件的时候,就不继续匹配。使用方法
<Switch>
<Route path="/about" component={About} />
<Route path="/home" component={Home} />
<Route path="/home" component={Test} />
</Switch>
6.2.5 Redirct
Redirct组件:一般写在所有路由注册的最下方,当所有路由都无法匹配时,跳转到Redirct指定的路由
<Switch>
<Route path="/about" component={About} />
<Route path="/home" component={Home} />
<Redirect to="/home" />
</Switch>
6.2.6 HashRouter和BrowserRouter
- 底层原理不一样
BrowserRouter使用的是H5的history Api,不兼容IE9及以下版本HashRouter使用的是URL的Hash值
- URL表现形式不一样
BrowserRouter的路径中没有#,例如localhost:3000/a/bHashRouter的路径中带#,例如localhost:3000/#/a/b
- 刷新后对路由state参数的影响
BrowserRouter没有影响,因为state保存在history对象中HashRouter刷新后会导致路由state参数的丢失
6.3 路由组件和一般组件的区别
- 写法不同
- 一般组件:
</Demo> - 路由组件:
<Route path="/demo" component={Demo}>
- 存放位置不同
- 一般组件:
components - 路由组件:
pages
- 接收到的props不同
- 一般组件:根据传入时的标签
- 路由组件:接收到三个固定属性
history:
go: function go(n)
goBack: function goBack()
goForward: function goForward()
push: function push(path, state)
replace: function replace(path, state)
location:
pathname: "/home"
search: ""
state: undefined
match:
params: Object { }
path: "/home"
url: "/home"
- 一般组件可以通过
withRouter加工为路由组件,withRouter的返回值是一个新组件,使用方法为:
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { withRouter } from 'react-router-dom'
class Header extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
</div>
)
}
}
export default withRouter(Header)
6.4 向路由组件传递参数
6.4.1 Params参数
传递:
{/* 路由连接携带参数 */}
<Link to={`/home/message/detail/${msgObj.id}/${msgObj.title}`}>{msgObj.title}</Link>
{/* 注册路由声明接收 */}
<Route path="/home/message/detail/:id/:title" component={Detail}/>
接收:
let {id, title} = this.props.match.params
6.4.2 Search参数
传递
<Link to={`/home/message/detail/?id=${msgObj.id}&title=${msgObj.title}`}>{msgObj.title}</Link>
<Route path="/home/message/detail" component={Detail}/>
接收
let {search} = this.props.location
let parse = qs.parse(search.slice(1))
let {id, title} = parse
需引入qs库
import qs from 'qs'
6.4.3 State参数
传递
<Link to={{pathname:'/home/message/detail', state: {...msgObj}}}>{msgObj.title}</Link>
<Route path="/home/message/detail" component={Detail}/>
接收
let {id, title} = this.props.location.state || {}
6.5 编程式路由导航
<Link to={`/home/message/detail/?id=${msgObj.id}&title=${msgObj.title}`}>{msgObj.title}</Link>
<button onClick={() => {this.pushShow(msgObj.id, msgObj.title)}}>push查看</button>
<button onClick={() => {this.replaceShow(msgObj.id, msgObj.title)}}>replace查看</button>
replaceShow = (id, title) => {
this.props.history.replace(`/home/message/detail/${id}/${title}`)
}
pushShow = (id, title) => {
this.props.history.push(`/home/message/detail/${id}/${title}`)
}
7 Redux
7.1 Redux介绍
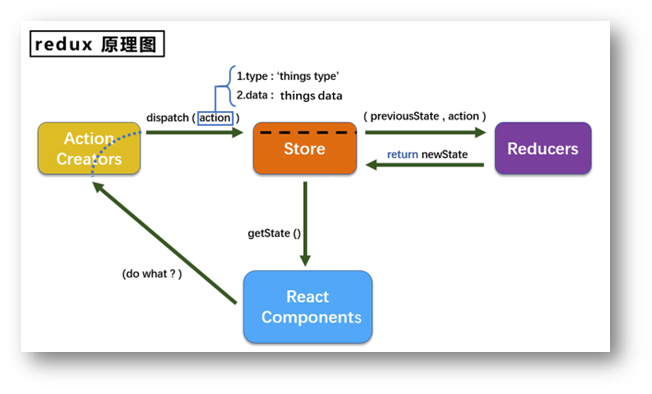
概念
- redux是一个专门用于做状态管理的JS库(不是react插件库)。
- 它可以用在react, angular, vue等项目中, 但基本与react配合使用。
- 作用: 集中式管理react应用中多个组件共享的状态。
什么情况下需要使用redux
- 某个组件的状态,需要让其他组件可以随时拿到(共享)。
- 一个组件需要改变另一个组件的状态(通信)。
- 总体原则:能不用就不用, 如果不用比较吃力才考虑使用。
7.2 redux的三个核心概念
7.2.1 action
action为动作的对象,包含2个属性
- type:标识属性, 值为字符串, 唯一, 必要属性
- data:数据属性, 值类型任意, 可选属性
7.2.2 reducer
reducer用于初始化状态、加工状态。加工时,根据旧的state和action, 产生新的state的纯函数。
7.2.3 store
将state、action、reducer联系在一起的对象
7.3 快速入门
创建store
import {legacy_createStore as createStore} from 'redux'
import countReducer from './count_reducer'
export default createStore(countReducer)
createStore API标记为@deprecated(废弃),并且添加了一个全新的legacy_createStore API,但是并没有添加弃用警告。此外该版本鼓励用户迁移到Redux Toolkit。import { configureStore } from "@reduxjs/toolkit";
创建reducer
import {INCREMENT, DECREMENT} from './constant'
let initState = 0
export default function countReducer(preState = initState, action) {
console.log(preState, action)
let {type, data} = action
switch (type) {
case INCREMENT :
return preState + data * 1
case DECREMENT:
return preState - data * 1
default:
return preState
}
}
创建action
import {INCREMENT, DECREMENT} from './constant'
export let createIncrementAction = data => ({
type: INCREMENT,
data
})
export let createDecrementAction = data => ({
type: DECREMENT,
data
})
使用
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import store from '../../redux/store'
import {createDecrementAction, createIncrementAction} from '../../redux/count_action'
export default class Count extends Component {
increment = () => {
let {value} = this.selectNum
store.dispatch(createIncrementAction(value * 1))
}
decrement = () => {
let {value} = this.selectNum
store.dispatch(createDecrementAction(value * 1))
}
incrementIfOdd = () => {
let {value} = this.selectNum
let count = store.getState()
if (count % 2 !== 0) store.dispatch(createIncrementAction(value * 1))
}
incrementAsync = () => {
let {value} = this.selectNum
setTimeout(() => {
store.dispatch(createIncrementAction(value * 1))
}, 500)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Count sum: {store.getState()}</h1>
<select ref={c => this.selectNum = c}>
<option value="1">1</option>
<option value="2">2</option>
<option value="3">3</option>
</select>
<button onClick={this.increment}>+</button>
<button onClick={this.decrement}>-</button>
<button onClick={this.incrementIfOdd}>increment if odd</button>
<button onClick={this.incrementAsync}>increment async</button>
</div>
)
}
}
注意,上面只是更新值,但不会更新页面,可以在index.js
store.subscribe(() =>{
root.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>
);
})
7.4 异步Action
安装redux-thunk
yarn add redux-thunk
修改store
import {legacy_createStore as createStore, applyMiddleware} from 'redux'
import countReducer from './count_reducer'
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
export default createStore(countReducer, applyMiddleware(thunk))
使用:
export let createIncrementAsyncAction = (data, time) => {
return (dispatch) => {
setTimeout(() => {
dispatch(createIncrementAction(data))
}, time)
}
}
7.5 react-redux
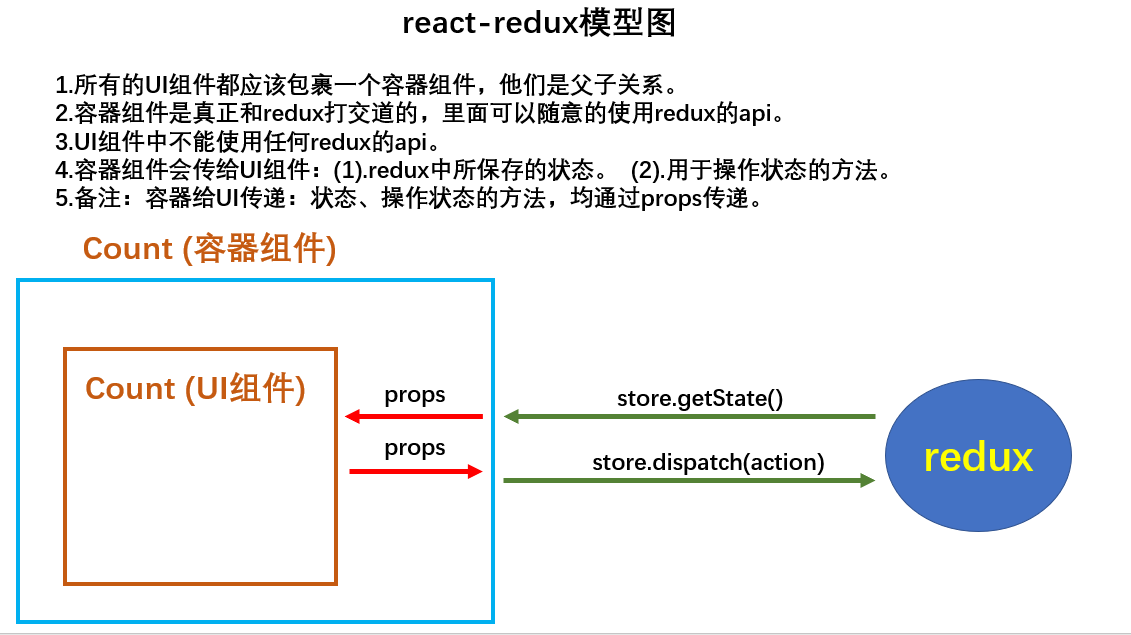
添加UI组件
import {connect} from 'react-redux'
import CountUI from '../../components/Count'
import {createIncrementAction, createDecrementAction, createIncrementAsyncAction} from '../../redux/count_action'
// mapStateToProps用于传递状态,返回是一个对象
// key作为传递给UI组件props的key,value作为传递给UI组件props的value
function mapStateToProps(state) {
return {
count: state
}
}
// mapStateToProps用于传递操作状态的方法,返回是一个对象
// key作为传递给UI组件props的key,value作为传递给UI组件props的value
function mapDispatchToProps(dispatch) {
return {
increment: (number) => {
dispatch(createIncrementAction(number))
},
decrement: (number) => {
dispatch(createDecrementAction(number))
},
incrementAsync: (number, time) => {
dispatch(createIncrementAsyncAction(number, time))
}
}
}
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(CountUI)
修改App.js
import './App.css';
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import Count from './containers/Count';
import store from './redux/store';
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<Count store={store}/>
</div>
)
}
}
使用:
import React, { Component } from 'react'
export default class Count extends Component {
increment = () => {
let {value} = this.selectNum
this.props.increment(value * 1)
}
decrement = () => {
let {value} = this.selectNum
this.props.decrement(value * 1)
}
incrementIfOdd = () => {
let {value} = this.selectNum
let count = this.props.count
if (count % 2 !== 0) {
this.props.increment(value)
}
}
incrementAsync = () => {
let {value} = this.selectNum
this.props.incrementAsync(value, 500)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Count sum: {this.props.count}</h1>
<select ref={c => this.selectNum = c}>
<option value="1">1</option>
<option value="2">2</option>
<option value="3">3</option>
</select>
<button onClick={this.increment}>+</button>
<button onClick={this.decrement}>-</button>
<button onClick={this.incrementIfOdd}>increment if odd</button>
<button onClick={this.incrementAsync}>increment async</button>
</div>
)
}
}
